Windows Artifacts and Forensics- The Cyber Blog India
Windows artifacts and forensics
Artifacts… what are they? Why are artifacts so important?
* 91.8% of traffic comes from computers using Windows as their Operating System.
* As an examiner or a practitioner, you will most likely encounter a system that runs Windows.
Artifacts, for an examiner, are the mines that can be minted for data. If you are familiar with something called the ‘windows registry’, you will know that this is the most invaluable source of forensic artifacts for all analysts. It keeps a track of all user activities and applications, which is all the information that an examiner needs to begin with. However, knowing binary logic is important because all windows registries are based on these binary values and their interpretation.
How to enter the windows registry?
- Press the Windows button + R to go to the run dialogue box,
- Type regedit
You are now in the windows registry.
How to navigate through the registry?
While you could use the open-source tools that are in flying numbers, will they ever make you a real Forensics Examiner? Nonetheless, to get to the real way of doing things, it is important to learn the basics.
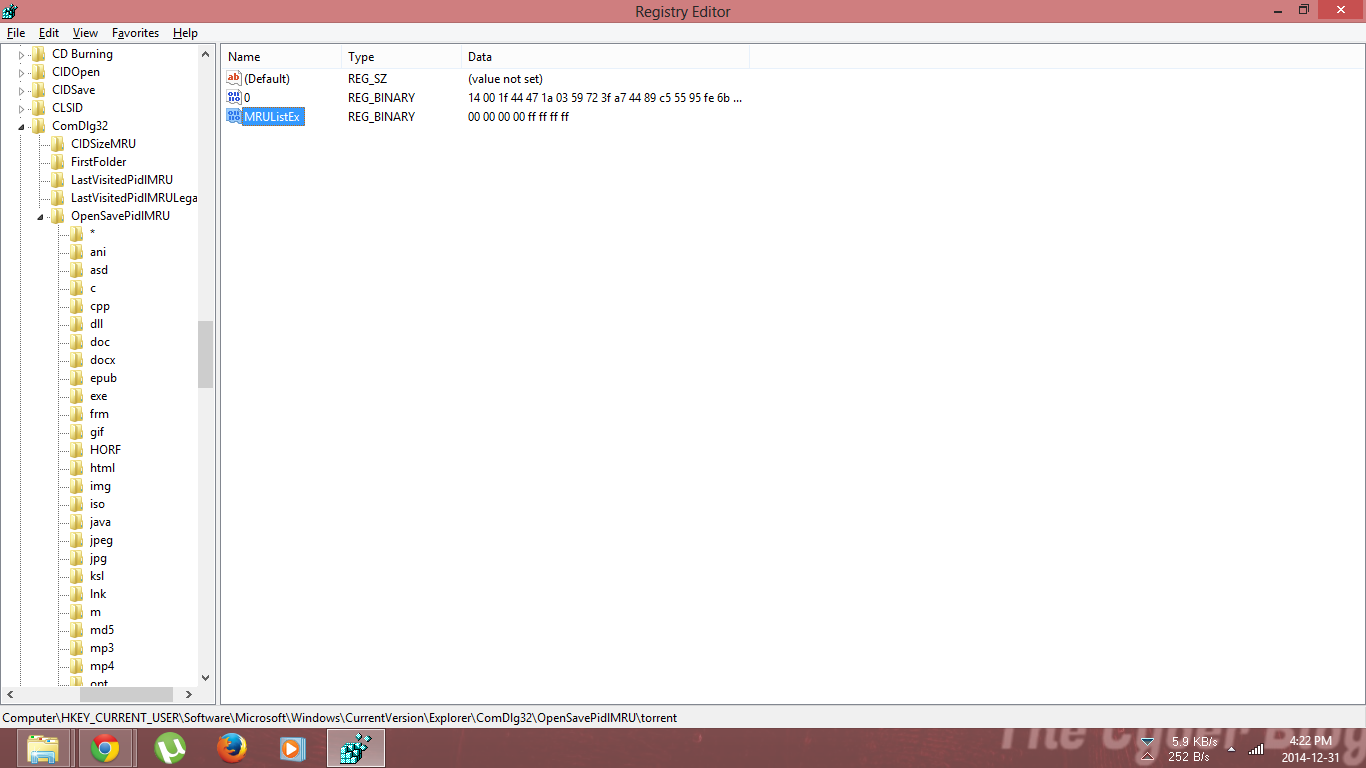
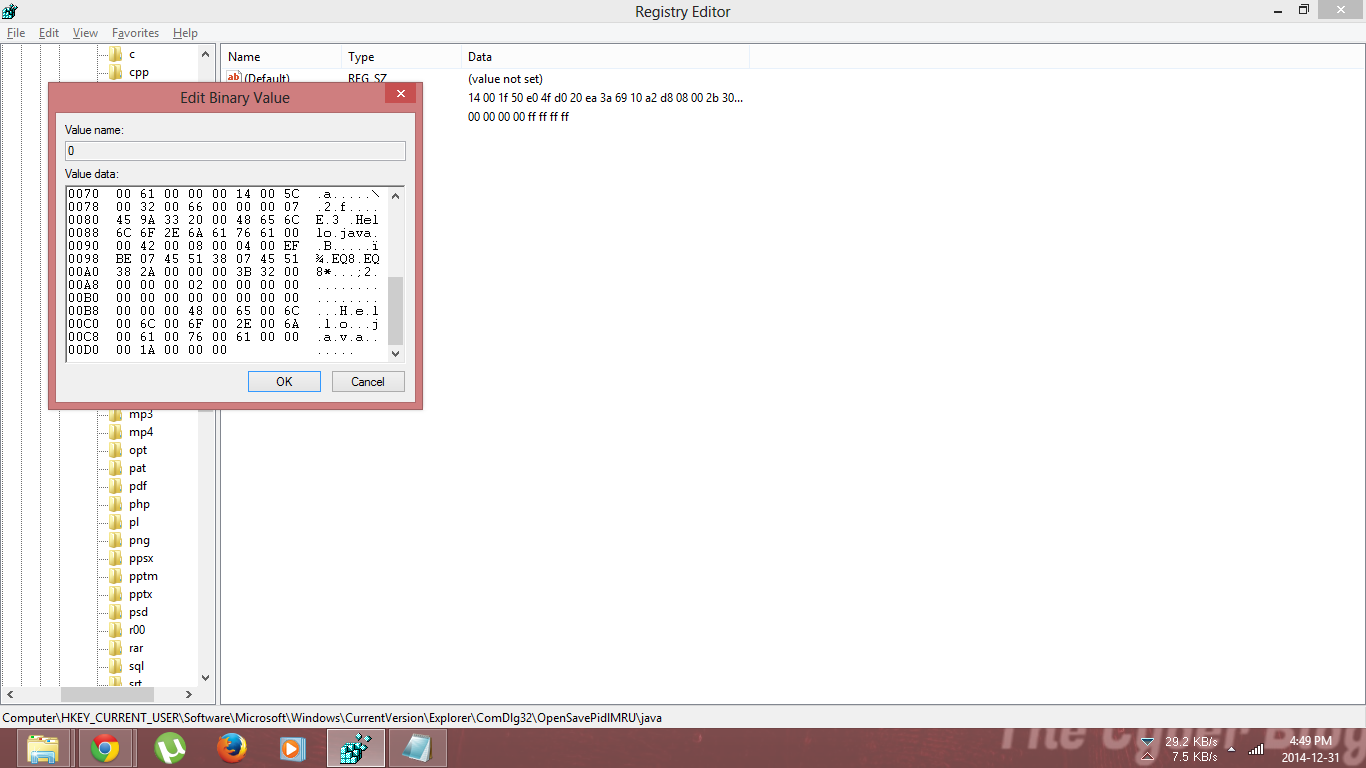
First, we will go through one type of registry to understand the process. (OpenSavePidlMRU)
- Go to the Windows Registry.
- Navigate to HKEY_CURRENT_USER>Software>Microsoft>Windows>Explorer>ComDlg32>OpenSavePidlMRU
- Click on the type of file you want to check and here on the left you have the files you can open to check the open/save history.
Therefore, using the same method, you can check other artifacts depending on your analytic skills.
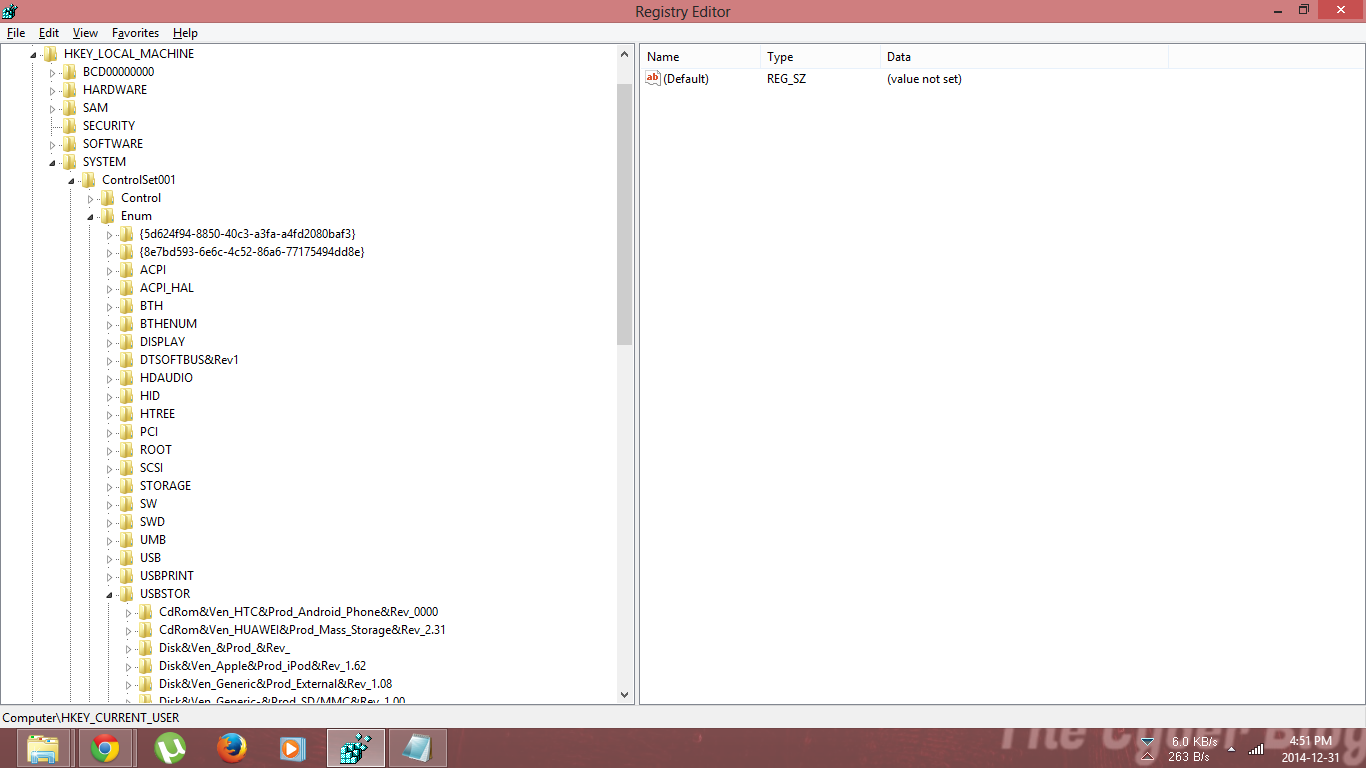
Now that you know how to go through applications, you can also go through USB devices.
- Go to the Windows Registry.
- Navigate HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE>SYSTEM>ControlSet001>Enum>USBSTOR
- Here, you can find a list of the devices ever connected.
- If you need you can use the popular USBDeview, which can give you a more arranged form of data.
Further, once you learn about all the artifacts, you should then learn how to read these artifacts.
The device IDs for USB mass storage devices in Usbstor.inf take the usual form for USB device IDs. This is composed by using the information in the USB device’s device descriptor:
USB\VID_v(4)&PID_d(4)&REV_r(4), where:
- v(4) is the 4-digit vendor code that the USB committee assigns to the vendor.
- d(4) is the 4-digit product code that the vendor assigns to the device.
- r(4) is the revision code.
Furthermore, you can also go over to the SQLite files in the User>AppData Folders and browse those databases for more information.
Hence, these are all the artifacts that you need to know to get ahead.